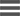Plantar Fasciitis
The plantar fascia is a tough, tendinous structure along the bottom of the foot that creates the arch of the foot. It extends from the heel bone, and then splits and fans out to attach itself to the toes.
Plantar fasciosis is a condition where the plantar fascia becomes painful from overstretching or overuse, causing pain in the heel and bottom of the foot. It can be aggravated by prolonged weight bearing activities (standing/walking/running) and is one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints, with 1 in 10 people experiencing this at some point in their lives. The peak age is between 40-60 years of age.
It can be associated with:
- High or low foot arches
- Obesity or sudden weight gain
- Tight Achilles tendon which connects the calf muscles to the heel
- Starting a new activity or increasing the intensity of an activity
- Wearing improper shoes with soles that are too soft/ too hard, do not fit well or offer poor arch support
The major complaint of plantar fasciosis is pain and stiffness in the heel and foot. The pain associated with this condition becomes more intense:
- In the morning when you step out of bed
- Walking after sitting or standing for some time
- Climbing stairs
- After exercise
Your Sports Physician will diagnose plantar fasciosis after reviewing your medical history and conducting a physical examination. An X-ray or MRI scan of the foot may be ordered at the discretion of your physician.
Although this can be an extremely painful condition, it is generally self-limiting with most cases resolving over 6-18 months. Treatment will be aimed at reducing your pain, keeping you fit and active and aiming to speed up recovery. These treatment measures include:
- Active Rest: reduces pain and prevents aggravating pain
- Ice: Rolling your foot over ice can be very effective in reducing pain
- Medications: NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) may be prescribed to help reduce pain and inflammation
- Exercise: calf and foot strengthening exercises
- Physical therapy may be recommended
- Supportive shoes and orthotics may also be recommended to reduce the pain while walking or standing
- Night splints can be suggested to help stretch the plantar fascia while sleeping
- Adjunctive treatments such as extracorporeal shock wave therapy may be considered by your Sports Physician
Surgical treatment is rarely if ever considered.